Speed equation in physics

Understanding Speed in Physics Speed is a measure of how fast an object is moving from one place to another. It tells us the rate at which distance is covered in a given amount of time. For example, when a…

Understanding Speed in Physics Speed is a measure of how fast an object is moving from one place to another. It tells us the rate at which distance is covered in a given amount of time. For example, when a…
Pivot Point Definition A pivot point in physics is a fixed point around which an object rotates or balances. It serves as the axis of rotation for a rigid body and is the reference point for calculating torque (rotational force).…
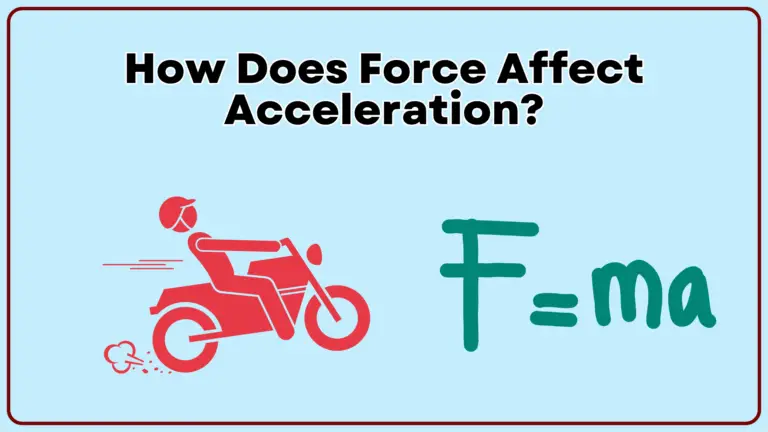
Force directly affects acceleration according to Newton’s Second Law of Motion. The law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. Newton’s Second Law The…
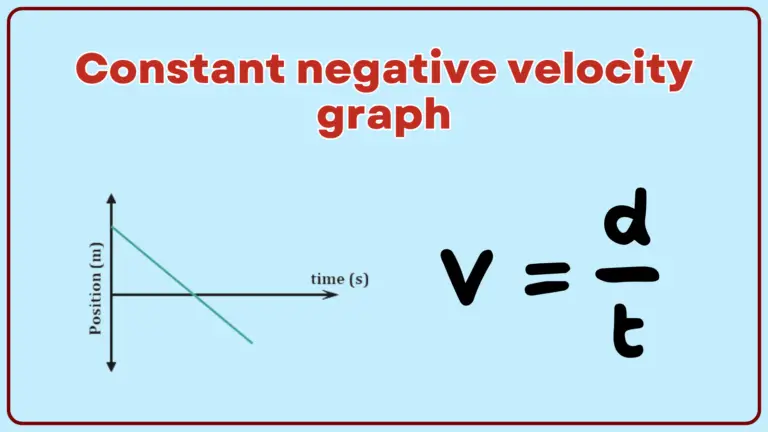
A constant negative velocity graph is a straight line with a negative slope on a position-time graph, representing an object moving at a constant speed in the opposite direction of the positive axis. Explanation In physics, velocity is a vector…
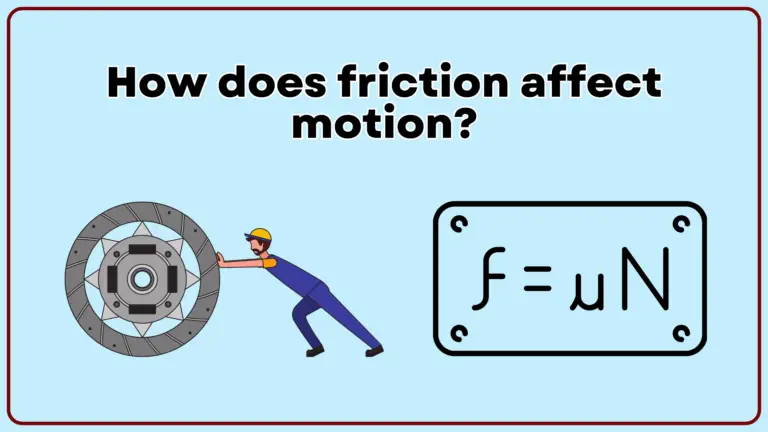
Friction is a force that opposes the relative motion between two surfaces in contact. It significantly affects motion by slowing down moving objects, preventing stationary objects from starting to move, and converting kinetic energy into thermal energy. Here’s a detailed…
Acceleration significantly changes the nature of an object’s motion by altering its velocity over time. This change can happen in three primary ways: Ways acceleration affect motion Let’s explore each of these effects in more detail: Increasing Speed When an…

During a free fall, the acceleration remains constant and is equal to the acceleration due to gravity (g), which is approximately 9.8 m/s² on Earth’s surface. This constant acceleration is directed downward towards the center of the Earth. Explanation To…

Acceleration directly affects tension in a system by increasing or decreasing the force required to change an object’s velocity. As acceleration increases, tension generally increases, and as acceleration decreases, tension typically decreases. Explanation To understand how acceleration affects tension, let’s…
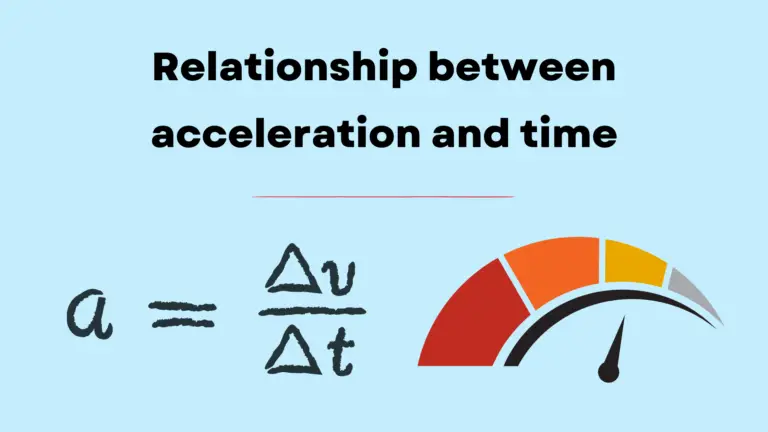
Acceleration can change with time in various ways, depending on the forces acting on an object and the specific situation. The relationship between acceleration and time is not always constant and can be described by different mathematical functions. How does…