In this article, we will learn an easy concept of How to find acceleration with mass and force? To understand this we will first briefly look into Newton’s Second Law of Motion. We will also learn the essential formulas, units, and steps needed to understand and solve physics problems involving acceleration, mass, and force.
Key Takeaways
- Newton’s Second Law of Motion: The force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration $(F = m a)$.
- Acceleration (a) can be calculated by dividing the net force (F) by the mass (m) of the object: $a = F / m$.
- Units:
- Force (F): newtons (N)
- Mass (m): kilograms (kg)
- Acceleration (a): meters per second squared (m/s²)
- Acceleration is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. Consider the signs and directions of forces when solving problems involving acceleration.
- If multiple forces are acting on the object, you need to determine the net force by adding or subtracting the individual forces, taking into account their directions.
How to find acceleration with mass and force?
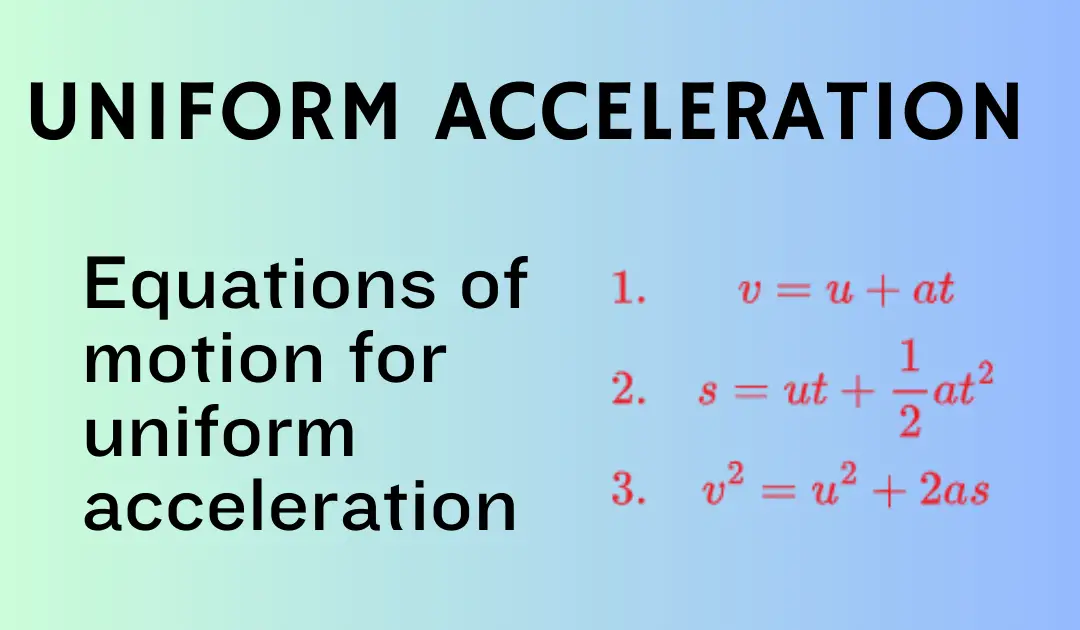
we will use Newton’s Second Law of Motion, which states that the force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
$F = m a$
Where:
- $F$ represents the force acting on the object (measured in newtons, N)
- $m$ represents the mass of the object (measured in kilograms, kg)
- $a$ represents the acceleration of the object (measured in meters per second squared, m/s²)
To find the acceleration of an object $(a)$ when given its mass $(m)$ and the force acting on it $(F)$, we can rearrange the formula like this:
$a =\frac{ F}{m}$
Step-by-step process to find the acceleration
- Identify the mass of the object (m). This should be given in kilograms (kg).
- Identify the net force acting on the object (F). This should be given in newtons (N). Note that if multiple forces are acting on the object, you need to find the net force by adding or subtracting the individual forces, taking into account their directions.
- Plug the values of mass (m) and force (F) into the formula for acceleration:
$a = F / m$ - Calculate the result. This will give you the acceleration of the object in meters per second squared (m/s²).
Points to remember
- Remember that acceleration is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction.
- If the problem requires you to find acceleration in a specific direction, make sure you consider the signs of the force components acting in that direction.
- Positive and negative signs indicate the direction of the force and the resulting acceleration.
Solved example
Let us learn how to find acceleration with mass and force with the help of a solved example.
Suppose you are given a 5 kg object, and a horizontal force of 20 N is applied to it. To find the acceleration:
- Identify the mass: m = 5 kg
- Identify the net force: F = 20 N
- Use the formula: a = F / m
- Calculate the acceleration: a = 20 N / 5 kg = 4 m/s²
So, the acceleration of the object is 4 m/s² in the direction of the applied force.
Quiz on this topic
Given below is a short 5-question quiz about the concepts discussed in this article. Test your knowledge about whatever you have learned on this topic of calculating acceleration when you have knowledge about mass and acceleration. Choose the correct option among the choices given in the question.