What is an Optically Denser and Rarer Medium?
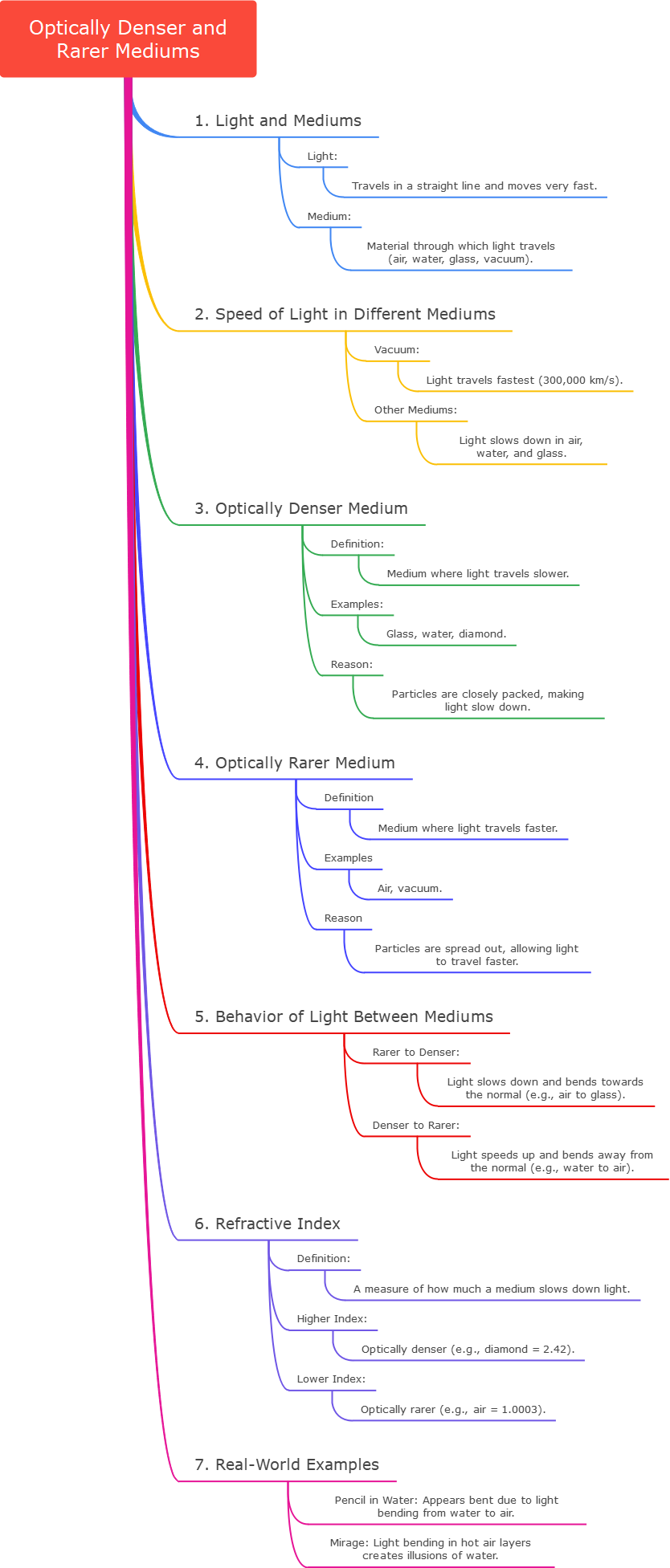
When studying light and how it travels, we often talk about how light moves through different mediums (or materials). Some materials make light slow down more than others. Based on this, we can classify materials into two types: optically denser and optically rarer mediums.
1. Light and How It Travels
- What is Light?
Light is a type of energy that allows us to see things. It travels in a straight line in all directions, and it moves very fast. - What is a Medium?
A medium is the material through which light travels. This could be air, water, glass, or even empty space (called a vacuum).
2. The Speed of Light in Different Mediums
- In a Vacuum (Like Space)
In a vacuum, there is nothing to slow down light. So, light travels the fastest in space, at about 300,000 kilometers per second (km/s). - In Air, Water, or Glass
When light enters a medium like air, water, or glass, it slows down a bit. This slowing down depends on the medium’s density.
3. What is an Optically Denser Medium?
An optically denser medium is a material in which light travels slower compared to other mediums.
- Examples:
- Glass
- Water
- Diamond
- Why is it Denser?
These materials have particles that are packed more closely together, so light has to interact with more particles as it passes through. This makes the light slow down.
4. What is an Optically Rarer Medium?
An optically rarer medium is a material in which light travels faster compared to denser mediums.
- Examples:
- Air
- Vacuum (empty space)
Why is it Rarer?
These mediums have particles that are spaced further apart, so light encounters fewer particles and can travel faster.
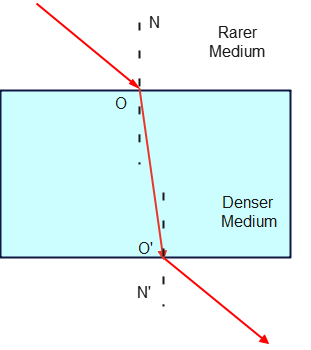
5. How Light Behaves When Moving Between Mediums
- From Rarer to Denser Medium
When light enters an optically denser medium from a rarer medium, it slows down and bends towards the normal. For example, when light moves from air (rarer) to glass (denser), it slows down and bends inward. - From Denser to Rarer Medium
When light moves from an optically denser medium to a rarer medium, it speeds up and bends away from the normal. For example, when light moves from water (denser) to air (rarer), it speeds up and bends outward.
6. Refractive Index: A Measure of Optical Density
- What is the Refractive Index?
The refractive index is a number that tells us how fast or slow light travels through a medium. A higher refractive index means the medium is optically denser, while a lower refractive index means the medium is optically rarer. - Examples of Refractive Indices:
- Vacuum: 1.0 (light travels fastest)
- Air: 1.0003
- Water: 1.33
- Glass: 1.5
- Diamond: 2.42 (light travels slowest)
7. Real-World Examples
- Water and Air
When you place a pencil in a glass of water, it looks bent or broken at the surface. This happens because light moves from water (denser) to air (rarer) and bends away from the normal. - Mirages in the Desert
In a hot desert, you may see a mirage, which looks like water on the ground. This happens because light bends differently in layers of air with different temperatures (optically rarer and denser air).
8. Summary
- Optically Denser Medium: A medium where light travels slower (e.g., glass, water).
- Optically Rarer Medium: A medium where light travels faster (e.g., air, vacuum).
- Refractive Index: A number that shows how much a medium slows down light.
By understanding how light behaves in different mediums, we can explain many natural phenomena, like why objects appear bent underwater or why we see rainbows!